How does a chatbot gets its information?
- Rules-based chatbots follow predefined scripts created by humans or AI.
- Some chatbots pull contextual information from CRMs or knowledge bases.
- Advanced chatbots gather user data during conversations to personalize responses.
- Machine learning models learn from large datasets and update with new information.
- External APIs provide real-time data like weather or account info.
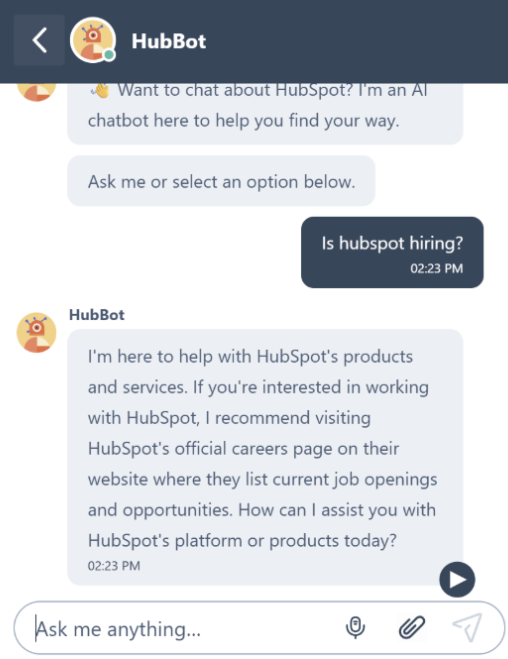
Little chat bubbles and boxes have started popping up on all sorts of websites. Visit Chewy, and you can click “Chat Live With Us” to ask why your dog food hasn’t shown up. At HubSpot, the adorable HubBot is ready to book a demo or share free training.
But who are you actually talking to? Those speedy responses are probably coming from a chatbot, not the Michael Phelps of typing.
What is a chatbot? It’s software that answers questions and helps customers with basic tasks. It’s also an excellent assistant. You can let your friendly chatbot track orders and collect client data, freeing up your to-do list, or at least shrinking it a little.
Chatbots might all look the same to users, but there are different types. Understanding how a chatbot works will help you decide if this technology is right for your business.
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a program that can have conversations with humans. Most chatbots on websites communicate through text, but some can talk to you over the phone, sometimes in convincingly human-like voices.
How does a chatbot work? The most advanced bots are powered by artificial intelligence (AI). They use a technique called natural language processing to interpret what you say and give human-sounding responses.
Type “I ordered blue pants, but these are covered in ugly polka dots,” and an AI chatbot might respond with something like, “That’s a bummer! Would you like me to start an exchange so you can get the right color?”
Other chatbots use a series of rules to understand your message and generate an appropriate, prewritten response. If you go off script by entering an unexpected message, you won’t get a useful reply.
HubBot is a classic example of a rules-based chatbot. Ask it if the company’s hiring, and it spits out a clearly preprogrammed response: “If you’re interested in working with HubSpot, I recommend visiting HubSpot’s official careers page on their website where they list current job openings and opportunities.” It can’t tell you about current job openings or anything that isn’t in its script.
Chatbot benefits
Customers want instant gratification, not endless hold times. Chatbots can respond immediately to their questions or route them to the right person if a problem is too complex. That means fewer disgruntled customers clogging your support queue.
Cost and scalability are two more major benefits of chatbots. These programs can do the work of a full support team for a fraction of the price, and they don’t need health insurance. And during back-to-school shopping and Black Friday sales, they can help you handle a sudden influx of inquiries.
Chatbot terms you should know
Like any technology, chatbots have their own jargon. Beef up your tech vocabulary with these terms:
Decision trees map out possible conversational paths between a chatbot and a human. When a chatbot asks, “Is there anything else I can help you with?” it might only have two branches: yes and no. Meanwhile, AI can respond with something more complex, like, “It depends.”
Human handovers happen when the chatbot steps back and lets a human take over.
Intent recognition lets AI chatbots read between the lines to figure out what the user wants. If you say, “This sundress is three sizes two big and I hate it,” the software may recognize that you want to return it, even if you don’t say it directly.
Natural language processing is an AI technique used to understand and respond to human language. It goes beyond the literal meaning of the words by interpreting context and even emotion.
An utterance is what a human says to a chatbot. For example, “I need to look up my order number” and “Can I change the shipping address?” are two separate utterances.
Types of chatbots
All chatbots have the same purpose: to hold natural conversations with humans and offer assistance. But they get there in different ways. Here are four common types of chatbots and how they work.
AI-powered chatbots
AI chatbots are the most intuitive and human-like. They’re trained with machine learning algorithms that analyze patterns in vast datasets. For example, you might feed the chatbot all your customer emails from the last five years so it learns to recognize common questions.
Rule-based chatbots
While an AI chatbot could potentially respond to any query, rule-based chatbots are much more structured. They use prewritten scripts that are triggered by certain words or phrases. If someone says, “I need to check my shipping status,” the chatbot can pull up their order information and update its script with accurate data.
However, these chatbots typically can’t answer any atypical or poorly phrased requests. If that same customer writes, “Where the heck are my shoes??” the chatbot might only respond with, “I’m sorry, I don’t understand.” Not very helpful, especially if the client is already running hot.
Menu-based chatbots
Some chatbots don’t even let users type in their own sentences and only offer a few prompts.
These chatbots are simple and take the guesswork out of interactions. Instead of typing a long story about how a box got crushed by the post office, the customer can choose “Replace order” from the menu. But menu-based chatbots aren’t very effective for nuanced or offbeat interactions.
Hybrid chatbots
Hybrid chatbots combine AI and rule-based programs. They have stock responses ready to go for common queries, like, “What’s the average shipping time?” For more sophisticated or vague questions, they rely on AI algorithms to suss out what the user means.
What is needed for a chatbot to work?
Here’s a quick breakdown of how chatbots function behind the scenes.
Every chatbot has a user interface. This is the side that customers see when they interact with the program. It’s usually a floating box that pops up in the corner of a web page. Some only have a few menu options, while others have a place for the client to type.
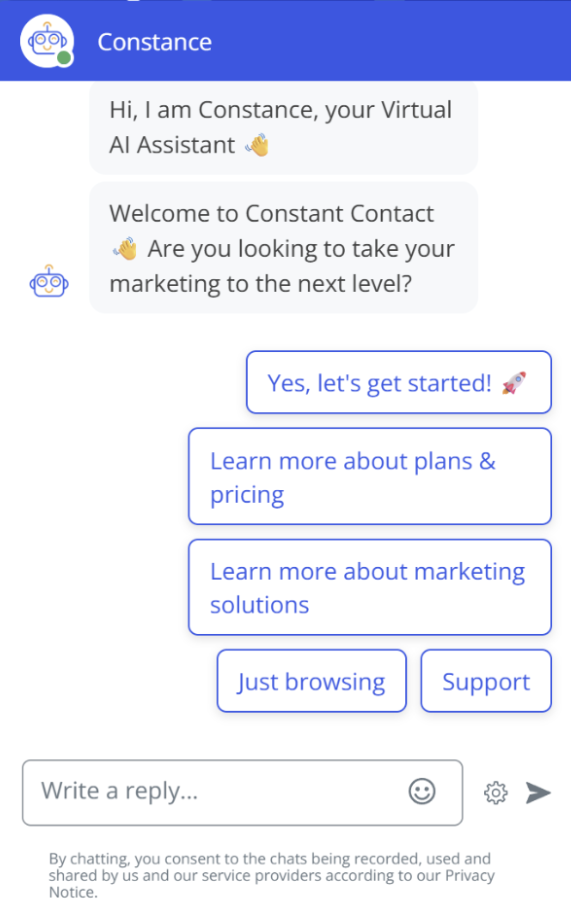
Here’s the user interface for Constant Contact’s chatbot:
Like HubBot, this hybrid chatbot, punnily named Constance, is represented by a cute robot avatar. Users can click one of five menu buttons or type a reply in the text box that follows them.
The inner workings become more complicated depending on the type of chatbot you use. Menu chatbots use a fixed set of pathways, such as “Check order status” or “Contact support.”
Rules-based chatbots are more advanced, using specific keywords or patterns to understand text. They then use decision trees to choose the best response, like this:
- Chatbot: Hello! I’m Steve, a chatbot who LOVES graphic design software. How can I help you today?
- Customer: I want to schedule a consultation.
- Chatbot: Great! Our sales team is usually available on Mondays and Wednesdays. When do you want to meet to talk about your project?
- Customer: Mondays.
- Chatbot: Thanks! I just need your email, and our sales manager Robert will be in touch pronto.
- Customer: Wednesdays.
- Chatbot: The team only has consultants from noon to two. Does that fit your schedule?
- Customer: None of these days work.
- Chatbot: No worries! Tell me the days you’re available, and we’ll find a time that works for everyone.
- Customer: I need to speak to support.
- Chatbot: What’s your question about?
- Customer: Technical issue.
- Chatbot: Oh no! Let me connect you with our IT team.
- Customer: Broken product.
- Chatbot: Can you give me the order number so I can look it up for you?
- Customer: Something else.
- Chatbot: Do you need help with pricing or returns? Or I can show you a demo of our new drawing tool!
AI chatbots have no set patterns, so every conversation is different. But no matter how smart they may seem, they have no original thoughts or true creativity. Not like humans, at least.
Instead, they use machine learning algorithms and deep learning to analyze tons of data, like application programming interfaces (APIs) connected to your customer relationship management (CRM) systems, product manuals, or even your website’s FAQ page. If you ask an AI chatbot for help with a return, for instance, it can pull from your website’s policy section to write an appropriate response.
How does a chatbot get its information?
There’s no universal chatbot information source that you can plug your software into. It depends on what kind you’re using and what you feed it. Here are a few options:
- Rules-based chatbots need a human, or maybe an AI generator, to create predefined scripts, which it selects based on keywords in the user’s conversation.
- Some bots draw contextual information from your CRM system or knowledge base in real-time. They might look up a customer’s address or past orders to customize their answers.
- Advanced chatbots gather user data during conversations and use it to personalize their responses. A customer who mentions they own a dog, for instance, might get pet-themed product recommendations later on.
- Machine learning models learn from vast datasets and update their responses when they get fresh information.
- External APIs let the chatbot access weather reports, account information, and other data in real-time.
For example, you can train Jotform’s AI agents with your website’s URL and uploaded PDFs. When someone asks who founded your company, the AI Agent will reference that page on your site, just like a human rifling through their memory.
How does a chatbot work?: A step-by-step breakdown
You don’t need to hire a software engineer or learn coding to design a chatbot. Here’s what the process looks like for Jotform’s Chatbot and AI Agents, both of which can interact with customers.
Start by using Jotform’s AI Chatbot Builder to create a custom agent. You can pick an avatar, set the level of chattiness, and even change the background color to match your website.
Train your AI agent by building a knowledge base or linking to your website. You can also upload documents or write questions along with ideal answers.
Once your chatbot is set up, here’s what a basic interaction might look like on an e-commerce website:
- The user enters the first message into the text box: “Hi. Does this come in black or blue?”
- The chatbot asks for more information: “Hello! Can you give me the product number or URL?”
- Once it has that data, the chatbot will search through its knowledge base for the product details.
- Chatbot: “Yes! That dress is available in black but not blue. Would you like to add it to your cart?”
- User: “Sure medium please”
- The chatbot can use an API to communicate with your e-commerce platform and update the cart with the dress in the correct size and color. Then it can respond, “Done! Is there anything else I can help you with?”
- User: “Nope”
- Chatbot: “Okay, have a great day!”
While some brands might prefer a professional conversation like this, others might consider it a little … dry. Boring, even. You can teach your agent your voice, so it can respond with more pizzazz. Instead of wishing someone a great day, for instance, your AI might answer with a sassy “Get back to shopping!”
Chatbot best practices
Like any technology, chatbots come with a learning curve. These tips will help you get the most out of yours and avoid frustrating customers:
- Use Jotform’s convenient chatbot templates to get started quickly. There are templates for everything from customer service to therapy and Shopify stores. With just a few clicks, you can have a functional AI Agent ready to chat with your customers.
- Be transparent. Add a short introduction, like, “Hey there! I’m Diego, an AI chatbot.” This lets users know exactly who, or more accurately, what, they’re speaking with. You should also teach your AI to hand off the conversation to a human whenever the user asks. That way, no one feels tricked, or worse, trapped, in an endless AI conversation.
- Update your chatbot regularly. Keep refreshing your knowledge base and uploading new documents. This prevents awkward situations, like the chatbot recommending a discontinued product or name-dropping a former CEO.
For a deeper dive and more tips, see the Jotform Chatbot Best Practices blog.
Speed up customer service with chatbots
Making customers wait on hold is so 2012. With chatbots, they can get instant answers from a smart robot that sounds just like your brand.
The best chatbots combine AI, natural language processing, and datasets for flawless human conversations. But for some brands, a simple menu bot is all it takes to get the job done. Research chatbot examples from your competitors and favorite brands to see what works.
Looking for an easy solution that can grow with your business? Try Jotform’s AI Chatbot. It’s totally customizable with no coding, and you can add many different data sources. Plus, it supports multiple languages and platforms, so you can use it wherever you need it.
Got a few minutes to spare? Build your first AI chatbot now. Yes, it’s that fast and simple.
FAQ: Common questions about how chatbots work
AI chatbots are the best choice for large companies with thousands of customers and products. They can handle complex queries and adapt on the fly as they get new information, like a hot item selling out in the middle of a Black Friday sale.
Chatbots focus on, well, chatting. They’re purely conversational and usually only manage basic tasks. AI Agents are more autonomous and capable of handling more complex workflows, like rerouting orders to a new address.
The AI Chatbot can get information from documents, knowledge bases, Q&As, or even from customer input. More data = more accurate answers.
This article is for website owners, digital marketers, and anyone looking to understand how chatbots work, their types and benefits, and how to create one with tools like Jotform AI.









































Send Comment: